Aurora I/O-Optimized eliminates per-request I/O charges for a flat storage rate. Here's how to calculate if switching saves you money.
Aurora I/O-Optimized vs Standard: Save 30-40% on AWS Database Costs (2026 Guide)
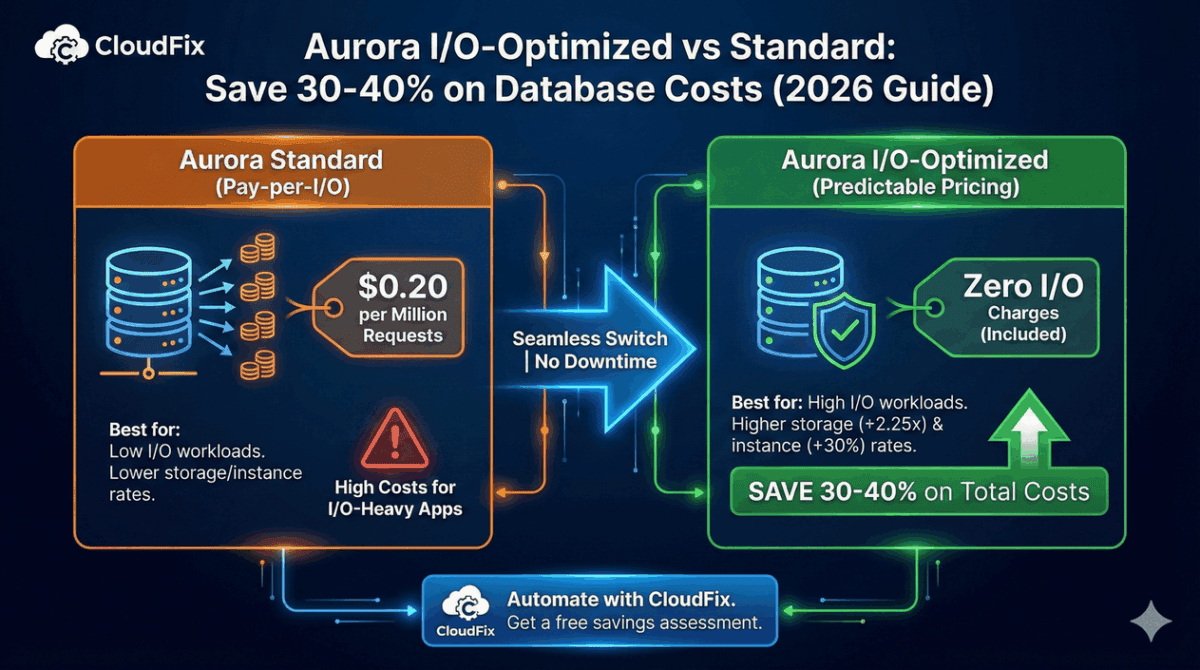
Aurora I/O-Optimized can cut your AWS database costs by 30-40% if you have I/O-heavy workloads. Instead of paying per million I/O requests, you pay a higher flat rate for storage with all I/O included.
The decision comes down to math: if your I/O costs exceed roughly 25% of your total Aurora spend, I/O-Optimized likely saves money. For databases with heavy read/write activity like e-commerce, IoT, analytics the savings can be substantial.
This guide covers how Aurora I/O-Optimized pricing works, when to switch, and how to migrate your clusters.
Aurora Standard vs I/O-Optimized Pricing
| Component | Standard | I/O-Optimized | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Storage | $0.10/GB-month | $0.225/GB-month | 2.25x more |
| I/O Requests | $0.20/million | Included | |
| Instance Hours | Base rate | +30% | 1.3x more |
Prices for Aurora PostgreSQL in us-east-1.
The tradeoff: I/O-Optimized charges more for storage and instances but eliminates I/O charges entirely. If your I/O costs are high enough, the elimination of per-request fees outweighs the increased storage and instance costs.
Aurora is one of 5 database optimizations most teams miss.
If you’re overpaying on Aurora I/O, you’re probably overpaying elsewhere too. Our 32-item checklist covers EBS, S3, RDS, DynamoDB, and more.
Download the Checklist →When I/O-Optimized Saves Money
General rule: If I/O costs exceed 25% of your total Aurora bill, I/O-Optimized likely saves money.
Good candidates:
- E-commerce databases with high transaction volume
- IoT applications ingesting sensor data
- Analytics workloads with heavy read patterns
- Social media platforms with constant read/write activity
- Any database where I/O is the largest cost component
Keep Standard:
- Low-traffic databases
- Development and test environments
- Databases where storage is the dominant cost
- Workloads with sporadic, unpredictable I/O patterns
Calculating Your Savings
To determine which configuration is cheaper, compare your costs under both models.
The Formula
Standard cost:
Instance cost + Storage cost + I/O cost
I/O-Optimized cost:
(Instance cost × 1.3) + (Storage cost × 2.25)
If I/O-Optimized cost < Standard cost, switch.
Example Calculation
Current workload:
- Instance: db.r6g.large ($0.29/hour × 730 hours = $211.70/month)
- Storage: 500 GB × $0.10 = $50/month
- I/O: 500 million requests × $0.20/million = $100/month
Standard total: $361.70/month
I/O-Optimized:
- Instance: $211.70 × 1.3 = $275.21/month
- Storage: 500 GB × $0.225 = $112.50/month
- I/O: Included
I/O-Optimized total: $387.71/month
In this example, Standard is cheaper. But watch what happens when I/O doubles:
High I/O workload (1 billion requests):
- Standard: $211.70 + $50 + $200 = $461.70/month
- I/O-Optimized: $275.21 + $112.50 = $387.71/month
Savings: $73.99/month (16%)
At 2 billion I/O requests, savings jump to $261.70/month (40%).
Quick Decision Table
| Monthly I/O Requests | I/O Cost (Standard) | Likely Winner |
|---|---|---|
| < 250 million | < $50 | Standard |
| 250-500 million | $50-100 | Calculate both |
| 500M – 1 billion | $100-200 | I/O-Optimized |
| > 1 billion | > $200 | I/O-Optimized |
Assumes moderate storage and instance costs. Your break-even will vary.
How to Check Your Current I/O Usage
Using AWS Cost Explorer
- Go to AWS Cost Explorer
- Filter by Service: Amazon RDS
- Group by Usage Type
- Look for
Aurora:StorageIOUsagecharges
If this line item is significant (>25% of total), you’re a candidate for I/O-Optimized.
Using CloudWatch
Check the VolumeReadIOPs and VolumeWriteIOPs metrics for your Aurora cluster:
aws cloudwatch get-metric-statistics \
--namespace AWS/RDS \
--metric-name VolumeReadIOPs \
--dimensions Name=DBClusterIdentifier,Value=your-cluster \
--start-time 2025-12-01T00:00:00Z \
--end-time 2025-12-31T00:00:00Z \
--period 2592000 \
--statistics Sum
Multiply the total by $0.20/million to estimate your I/O costs.
How to Switch to I/O-Optimized
Switching configurations is straightforward and requires no downtime.
Using AWS Console
- Open the RDS console
- Select your Aurora cluster
- Click Modify
- Under Storage type, select Aurora I/O-Optimized
- Choose Apply immediately or schedule for maintenance window
- Click Modify cluster
Using AWS CLI
aws rds modify-db-cluster \
--db-cluster-identifier your-cluster-name \
--storage-type aurora-iopt1 \
--apply-immediately
Migration Notes
- No downtime required
- Change takes effect within minutes
- You can switch back to Standard anytime
- 30-day minimum before switching back (to prevent gaming the system)
Frequently Asked Questions
Does I/O-Optimized affect performance?
No. I/O-Optimized is purely a pricing change. Your database performance, latency, and throughput remain identical.
Can I switch back to Standard?
Yes, but you must wait 30 days after switching to I/O-Optimized before switching back.
Does this work with Aurora Serverless?
I/O-Optimized is available for Aurora Serverless v2. For Serverless v1, only Standard pricing applies.
What about Reserved Instances?
Reserved Instances work with both configurations. The 30% instance cost increase for I/O-Optimized applies to the base rate before RI discounts.
How do I know my exact break-even point?
Use AWS’s pricing calculator or analyze your Cost and Usage Report. CloudFix automatically calculates this for all your Aurora clusters.
Does this apply to both MySQL and PostgreSQL?
Yes. I/O-Optimized is available for both Aurora MySQL-Compatible and Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible editions.
What about Global Databases?
I/O-Optimized works with Aurora Global Databases. Each region can be configured independently.
Real-World Savings
Case study: Graphite.dev
Graphite.dev, a code review platform, switched to I/O-Optimized and reported 90% cost reduction on their Aurora database. Their workload was exceptionally I/O-heavy, making them an ideal candidate.
Typical savings range: 30-40% for I/O-intensive workloads.
CloudFix customers have seen savings up to 30% on Aurora costs after switching appropriate clusters to I/O-Optimized.
Automate with CloudFix
Analyzing I/O patterns across all your Aurora clusters, calculating break-even points, and tracking which clusters have been optimized is time-consuming manual work.
CloudFix automatically:
- Analyzes 90 days of Cost and Usage Report data
- Calculates Standard vs I/O-Optimized costs for each cluster
- Identifies clusters with 15%+ savings potential
- Surfaces recommendations in the dashboard
- Executes the switch via AWS Change Manager
The CloudFix Aurora I/O Optimizer fixer is found under Advanced → RDS Retype IO Optimize.
Get a free savings assessment to see how much you’re overspending on Aurora I/O.
Related Resources:
- AWS Aurora I/O-Optimized Documentation
- Aurora Pricing
- AWS Blog: Estimate Aurora I/O-Optimized Savings
Is Aurora I/O-Optimized right for your clusters?
The math depends on your I/O patterns. CloudFix analyzes your actual usage and shows exactly which clusters will save money — plus 30+ other optimizations. Free assessment.