CloudFront compression can cut your data transfer costs by 65-80%. Here's how it works, when to enable it, and how to configure it correctly.
CloudFront Compression: Save 65-80% on CDN Costs (2026 Guide)
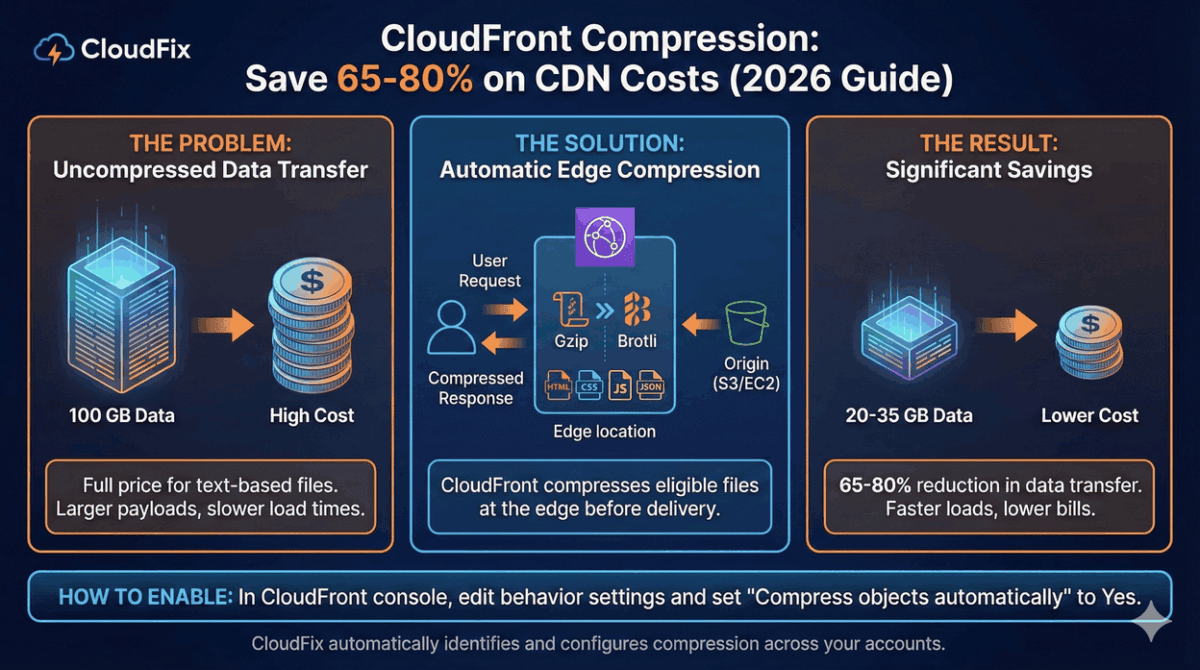
CloudFront compression reduces data transfer costs by 65-80% for text-based content. If you’re not using it, you’re paying full price for files that could be a fraction of the size.
Since 2015, CloudFront has supported automatic compression using gzip and Brotli. These algorithms compress HTML, CSS, JavaScript, JSON, and other text files before delivering them to users. The result: smaller payloads, faster load times, and significantly lower CloudFront bills.
This guide covers how compression works, which files benefit most, and how to enable it without breaking anything.
How Much Can You Save?
CloudFront charges based on data egress, ie the amount of data transferred from edge locations to users. Compression reduces the size of that data.
Typical compression ratios by file type:
| File Type | Compression Ratio | Cost Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| JavaScript | 77% | Pay for 23% of original |
| HTML | 70-80% | Pay for 20-30% of original |
| CSS | 70-80% | Pay for 20-30% of original |
| JSON | 70-85% | Pay for 15-30% of original |
| SVG | 50-70% | Pay for 30-50% of original |
| XML | 60-80% | Pay for 20-40% of original |
According to AWS, a typical web page with mixed text, scripts, and images sees overall payload reduction approaching 80%.
Example calculation:
Without compression: 100 GB data transfer × $0.085/GB = $8.50/month
With 70% compression on text files (assuming 60% of content is compressible):
- Compressible: 60 GB → 18 GB after compression
- Non-compressible: 40 GB
- Total: 58 GB × $0.085/GB = $4.93/month
Savings: 42% on CloudFront data transfer
For high-traffic sites, these savings compound quickly. A site transferring 10 TB/month could save $3,000-4,000 annually just by enabling compression.
How CloudFront Compression Works
When compression is enabled, CloudFront automatically compresses eligible files at the edge:
- User requests content: Browser sends
Accept-Encoding: gzip, brheader indicating it supports compression - CloudFront checks cache: If compressed version exists in cache, serve it immediately
- Cache miss: fetch from origin: CloudFront retrieves file from your origin (S3, EC2, etc.)
- Compress and cache: CloudFront compresses the file, caches both versions, and returns the compressed version
- Subsequent requests: Compressed version served directly from cache
CloudFront stores both compressed and uncompressed versions. Users whose browsers don’t support compression (extremely rare in 2026) get the uncompressed version.
Compression Algorithms
CloudFront supports two compression algorithms:
Gzip
- Universal browser support
- Good compression ratios (60-80%)
- Fast compression/decompression
Brotli
- Better compression (15-25% smaller than gzip)
- Supported by all modern browsers
- Requires HTTPS
Enable both. CloudFront automatically serves Brotli when supported, falling back to gzip for older clients.
What Gets Compressed (and What Doesn’t)
CloudFront only compresses files with specific Content-Type headers. This prevents attempting to compress already-compressed binary files.
Compressed file types include:
text/htmltext/csstext/javascript/application/javascriptapplication/jsontext/xml/application/xmlimage/svg+xmltext/plainapplication/x-font-ttffont/opentype
NOT compressed (already compressed or binary):
image/jpeg,image/png,image/gif,image/webpvideo/*(all video formats)audio/*(all audio formats)application/zip,application/gzipapplication/pdf
File size requirements:
- Minimum: 1 KB (files smaller than 1 KB aren’t worth compressing)
- Maximum: 10 MB
How to Enable CloudFront Compression
Prerequisites
Compression requires:
- Cache policy with compression enabled: Both
EnableAcceptEncodingGzipandEnableAcceptEncodingBrotliset to true - TTL greater than zero: Files must be cacheable (if TTL = 0, CloudFront won’t compress)
- Compress Objects Automatically enabled: In the cache behavior settings
Using AWS Console
- Open the CloudFront console
- Select your distribution
- Go to Behaviors tab
- Edit the default behavior (or relevant cache behavior)
- Under Cache key and origin requests:
- Select or create a cache policy with compression enabled
- Set Compress objects automatically to Yes
- Save changes
Using AWS CLI
Create a cache policy that enables compression:
{
"CachePolicyConfig": {
"Name": "Compression-Enabled-Policy",
"MinTTL": 86400,
"MaxTTL": 31536000,
"DefaultTTL": 86400,
"ParametersInCacheKeyAndForwardedToOrigin": {
"EnableAcceptEncodingGzip": true,
"EnableAcceptEncodingBrotli": true,
"HeadersConfig": {
"HeaderBehavior": "none"
},
"CookiesConfig": {
"CookieBehavior": "none"
},
"QueryStringsConfig": {
"QueryStringBehavior": "none"
}
}
}
}# Create the cache policy
aws cloudfront create-cache-policy \
--cache-policy-config file://cache-policy.json
# Update distribution to use the policy
aws cloudfront update-distribution \
--id E1A2B3C4D5E6F7 \
--distribution-config file://distribution-config.json \
--if-match ETAG_VALUEVerify Compression is Working
Test with curl:
curl -I -H "Accept-Encoding: gzip, br" https://your-domain.com/script.jsLook for
Content-Encoding: brContent-Encoding: gzipIf you see neither, compression isn’t working. Check your cache policy and TTL settings.
CloudFront compression takes 5 minutes. What else are you missing?
Our 30-plus checklist covers the highest-impact AWS optimizations — ranked by savings and effort. CloudFront compression is just one of the quick wins.
Get the ChecklistCommon Problems and Fixes
Compression not applying
Problem: Files are served uncompressed despite enabling compression.
Causes and fixes:
- TTL is zero: Set MinTTL > 0 in your cache policy
- Wrong Content-Type: Ensure your origin sends correct Content-Type headers
- File too small: Files under 1 KB won’t be compressed
- Origin already compresses: If your origin sends
Content-Encoding: gzip, CloudFront won’t double-compress. Either let CloudFront handle compression or let the origin do it, not both.
Mixed results across files
Problem: Some files compress, others don’t.
Cause: Different cache behaviors may have different settings.
Fix: Review all cache behaviors in your distribution. Each path pattern (e.g., /api/*, /static/*) has its own compression settings.
Origin compatibility issues
Problem: Origin returns already-compressed content inconsistently.
Best practice: Configure your origin to serve uncompressed content and let CloudFront handle compression. This ensures consistent behavior and optimal caching.
For S3 origins: Upload files uncompressed. For EC2/ALB origins: Disable origin compression.
Performance Impact
Some teams worry about compression overhead. Don’t.
Decompression is nearly instant: Studies show gzip decompression is orders of magnitude faster than network transfer time. Users benefit from faster page loads even accounting for decompression.
No server-side overhead: CloudFront compresses at the edge, not at your origin. Your EC2 instances or Lambda functions aren’t doing extra work.
Cache hit ratio remains high: Compressed and uncompressed versions are cached separately. The vast majority of requests hit cache regardless.
CloudFront Security Savings Bundle
If you’re spending significantly on CloudFront, consider the CloudFront Security Savings Bundle:
- Commit to a monthly CloudFront spend for one year
- Get up to 30% discount on CloudFront charges
- Receive 10% of your commitment as AWS WAF credits
Example: $70/month commitment = $100 worth of CloudFront + $7/month WAF credits
This stacks with compression savings. Enable compression first to reduce your baseline, then commit to the reduced spend level.
Flat-Rate Pricing Plans (New in 2025)
AWS now offers flat-rate CloudFront plans with no overage charges:
| Plan | Monthly Cost | Data Transfer | Requests |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free | $0 | 100 GB | 1M |
| Pro | $15 | 50 TB | 10M |
| Business | $200 | 50 TB | 125M |
| Premium | $1,000 | 50 TB | 500M |
These plans include WAF, DDoS protection, and Route 53 DNS. If your usage is predictable and you want cost certainty, flat-rate may be worth evaluating.
However, for most customers, pay-as-you-go with compression enabled remains the best value.
Enable Compression at Scale with CloudFix
Finding all CloudFront distributions without compression and configuring them correctly takes time, especially across multiple AWS accounts.
CloudFix automatically:
- Scans all accounts for CloudFront distributions
- Identifies distributions where compression can be safely enabled
- Excludes distributions with explicit no-compression policies
- Configures compression with compatible cache policies
- Tracks savings across your organization
The CloudFix “CloudFront Turn On Compression” fixer handles the complexity so you don’t have to audit each distribution manually.
Get a free savings assessment to see how much you’re overspending on CloudFront data transfer.
How much are you overspending on AWS?
CloudFront compression is one of dozens of one-click fixes CloudFix implements automatically. See your total savings across all services — free assessment, no commitment.